Installing and Flashing Windows Correctly
If you don’t include housewrap, use a sill pan, and flash the flanges, the work is far from watertight.

Given the fact that windows create large holes in a house’s exterior, I’m always shocked to see how many builders in our area don’t install them correctly. In the nine years that I’ve been building and renovating homes, I’ve seen windows that haven’t been integrated with the housewrap, improperly flashed installations, and even windows with no flashing at all. Not only does improper installation affect the durability and warranty of the windows, but it also exposes the wall cavity to moisture problems.
Like any builders, my crew and I want to use efficient practices that won’t negatively affect the quality of our work. For us, that means using a pragmatic approach to installing windows with worst-case scenarios and long-term durability in mind.
Water Gets Behind All Siding, So Window Flashing Is The Next Line Of Defense
Based on conversations with subcontractors and local building officials, we’ve concluded that the reasons windows aren’t installed correctly often stem from an unrealistic expectation about the effectiveness of siding in keeping moisture out of the wall cavity. What many window installers don’t realize is that no matter how well siding is installed, moisture finds its way between it and the housewrap.
When moisture ends up on a layer as slick as housewrap, it does a logical thing: It slides down the wall. Once that moisture reaches the window, it easily finds its way into the rough opening through even the tiniest holes. Moisture that leaks into a wall cavity causes mold to grow. Mold is bad, for materials and for humans. That’s why we do everything we can to keep water moving out and away from the window by integrating it with the housewrap.
Read The Window Manufacturer’s Installation Guidelines
Most window manufacturers recognize the disastrous effect improper installation of their products can have on a home, including significant energy loss. That’s why they provide detailed installation instructions for their products. Following these instructions helps to keep the wall cavity dry and fulfills the window manufacturer’s warranty.
Although the photos show my crew installing metal-clad windows with integral flanges, the steps outlined here offer a look at fundamental elements found in most manufacturers’ installation guidelines. They address forming the waterproof sill pan, shimming the window so that it works properly, and flashing the flanges to shed water. These steps will receive LEED points as well.
We figure that our sillpan and flashing approach adds about 10 minutes to the installation time for each window and an average of $15 in materials for each double-hung unit. That’s relatively cheap insurance for such a large investment.
What To Do When Guidelines Conflict
These days, every housewrap, flashing-tape, and window manufacturer has a specific set of installation guidelines that must be followed to uphold each respective product’s warranty. So what do you do when they contradict one another?
We follow contributing editor Mike Guertin’s advice and use the most-restrictive protocol. For instance, when the window manufacturer shows no flashing details, we follow the tape or housewrap instructions. When one set of instructions calls for a simple flat sill pan and another calls for a sloped pan, create a sloped pan. It’s unlikely someone will claim you didn’t follow the instructions by doing more than is called for.
When in doubt, though, follow the window manufacturer’s instructions. The International Residential Code (R613.1) requires windows to be “installed and flashed according to manufacturers’ instructions.” If there’s ever a problem, you’ve done what was required by the building code.
Prepare The Rough Opening With Housewrap And Pan Flashing

We make our pan flashing on site with beveled siding and self-adhesive flashing tape using Typar’s 9-in. wide Flashing Flex to flash 2×6 walls because it allows us to form a seamless pan that contours to the sill. Other brands and widths are also available.
The Top Tab Folds Up, Not In
| First, cut across the header, then down the center. |
Make a horizontal cut and two angled cuts to the sill. |
 |
 |
|
Staple the tabs down, then cut the top tab. |
Fold up the top tab, and tape it out of the way. |
 |
 |
Site-Made Pan Flashing
Beveled siding creates a sloped sill. After wrapping the opening, we nail a piece of siding along the rough sill with 13⁄4-in. roofing nails. Be sure to add the thickness of the siding to the window’s height when framing the rough opening. Self-adhesive flashing tape goes on next. In cold weather, we apply spray adhesive (also called “primer”) to improve the tape’s adhesion. The Flashing Flex tape we’re using here calls for 3M’s Super 77 adhesive. We run flashing tape tight to the inside of the opening and 10 in. up each trimmer stud, then fold the rest over the housewrap. We sometimes staple the corners of the tape to prevent them from moving.
 |
 |

Ready-Made Pan Flashing

For us, making sill pans on site is efficient and cost effective. But there are manufactured pan-flashing systems available, such as Dow’s Weathermate Sill Pan, shown here ( www.dow.com ; $5). This can be an economical option if you don’t have a lot of windows to install. They come in various sizes to fit the opening’s width.
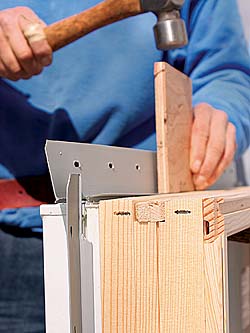
Caulk, Shim, And Nail The Window In Place
With the rough opening set, it’s time to install the window. Most manufacturers require the side and top flanges to be caulked to the perimeter of the rough opening. They illustrate adding the caulk to the flange, but we like to add it to the building instead so that it doesn’t get all over our hands as we put the window in. Regardless, make sure there’s a good seal around the flange. Get the window fully nailed off before the caulk dries.
Lap The Tape Shingle Style
Self-adhesive flashing tapes generally break down into two types: asphalt and butyl-based. Asphalt-based tape can damage certain types of vinyl, so check the window’s specs before using it. Butyl tape is easier to work with. It doesn’t have an aggressive initial tack, but its adhesiveness increases over time. When possible, we use tapes made by the manufacturer of the housewrap we’re using because the products are designed to work together.
| Extra protection for the head jamb. The head jamb is the most-vulnerable part of the window, which is why these windows come with a drip cap that adds a layer of protection. A similar cap can be made with flashing tape and aluminum coil stock.
|
The sides run long. Run flashing tape 4 in. to 5 in. past the top and bottom flanges. Make sure the tops of the side pieces stay at least 1 in. short of the top of the head piece so that the head piece will have a good, continuous bond with the sheathing. For windows with integral flanges, like the ones we’re installing here, butt the tape tight to the jamb.
|
 |
 |
| Tape the top. Roll tape over the top flange, letting it run past the side pieces by 2 in. to 3 in. Once the top piece is in place, fold down the housewrap tab. Tape along the bottom of the flap and at the corners with housewrap tape. Leave the bottom flange tape-free. The window is now ready for casing and siding. |
 |
 |
Mechanical Flanges Require Extra Attention
Not all flanged windows are made the same. The windows shown in this article have an integral nailing flange, which means that the flange is part of the window’s exterior cladding. Integral flanges are a good design because there aren’t seams or joints for water to sneak past. Hinged (photo, left)) and non-hinged (photo, right) mechanical flanges are also found on vinyl and metal-clad windows. Although these flange styles aren’t inferior to integral flanges, they have a few vulnerable areas that require extra attention during installation. Mechanical flanges are sometimes also call applied flanges. — by Mike Guertin
 |
 |

Mechanical flanges fit into grooves around the window jamb. They rely on a ribbed spline to stay engaged in the groove. The spline and a narrow gasket work together to keep out water. Hinge-style flanges are shipped folded against the frame, which leaves the corners incomplete. Manufacturers supply metal or plastic corner pieces to be applied and caulked once the window is hung. Non-hinged-style flanges overlap to form the flange corner. One benefit of mechanical flanges is that if they become damaged during installation, they are easy to replace. You install them by tapping a wood block along the inside tab. The downside is that they can become disengaged after installation for a variety of reasons (for example, the siding installer pushes or bumps the jamb, or someone steps on the sill before it’s shimmed in place).
To reduce the chance of window leaks, I make sure that everyone who works around them is aware of damage areas. I also shim around the window jamb’s perimeter every 6 in. and screw through the jamb and shims into the framing. Finally, (1.) I lap the flashing tape about 1⁄4 in. onto the side jambs and then over the flange and housewrap. At the window head, (2.) I run the tape over the jamb and down onto the window face by 1⁄8 in. to 1⁄4 in. I then install metal cap flashing over the head-flashing tape (3.) to conceal the tape.
|
 |

|

More on Windows:
Drip Cap Design and Installation – The lowly drip cap needs to be taken more seriously to prevent leaks and rot.
Flashing for Old Windows – How do you get a good weathertight seal on old windows that don’t have a flange?
Leak-free Windows Series: Sill Pan Flashing Options – Pre-formed or site-built, pan flashing channels water out where it won’t rot the sills under windows or the floors under doors.
Watertight window flashing – Q: When installing new windows, I believe it is considered good practice to allow the head flashing above the window trim to overhang a little bit on each side. This …
Window Flashing – A collection of articles on window flashing.
Window-Opening Preparation – Protecting the rough opening helps with air-sealing and water management.












View Comments
In cold and warm weather its a good Idea to heat the fortiflash with a heat gun after installation. It activates the adheasive making a superior bond. It does not take much heat so be careful not to burn the flashing.